for ( ![]() ), (
), ( ![]() ), (
), ( ![]() ), and (
), and ( ![]() )
respectively.
)
respectively.
where ![]() .
.
The interpolators and their spectra evaluated here are (assuming unity sample grid distance)[3][4]:
for ( ![]() ), (
), ( ![]() ), (
), ( ![]() ), and (
), and ( ![]() )
respectively.
)
respectively.
where ![]() .
.
Table i lists the theoretically derived coherence and
1-look phase noise
introduced by the first three and the last of these interpolators for
one and two
dimensions. ERS range signal parameters have been used for both
dimensions with uniformly weighted spectrum
and oversampling ratio of
![]() (in real systems,
azimuth oversampling is slightly higher than in range), i.e.\
(in real systems,
azimuth oversampling is slightly higher than in range), i.e.\
![]() .
.
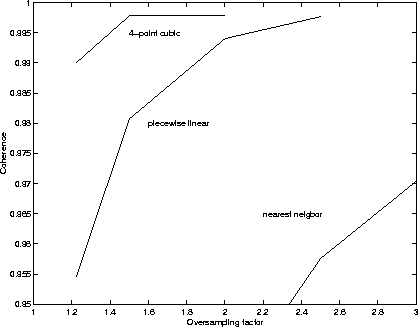
Figure 3: Improvement of 2-D interpolation for oversampled input data
(same oversampling factor in range and azimuth)
Often, SAR data are oversampled by a higher factor before an interferogram is computed, be it either to avoid undersampling of the interferogram or as a consequence of baseline dependent spectral shift filtering. In these cases the requirement on the interpolator is relaxed. Figure 3 shows how decorrelation reduces with oversampling.
Table i: Theoretically and simulation
derived influence of different 1-D and 2-D
interpolators on interferogram coherence and phase noise (phase standard
deviation without multi-looking)
Figure 4: Simulated interferograms using four kernels: nearest
neighbor, piecewise linear, 4-point cubic convolution, and
6-point cubic convolution.